Views: 15 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-12-10 Origin: Site
Powder metallurgy (PM) technology is widely used in the preparation of brake pads due to its ability to produce components with precise dimensions, excellent performance, and cost efficiency. This process has proven particularly advantageous in automotive, rail transit, and industrial machinery applications, where high friction performance, wear resistance, and heat dissipation are critical.
Powder metallurgy brake pads are typically composed of a matrix of iron-based or copper-based powders, combined with friction enhancers, lubricants, and fillers. The metal powders provide mechanical strength, while the added components ensure the frictional and thermal properties meet application-specific requirements. For instance, graphite is commonly used as a lubricant, and ceramics or carbides can be incorporated to improve wear resistance.

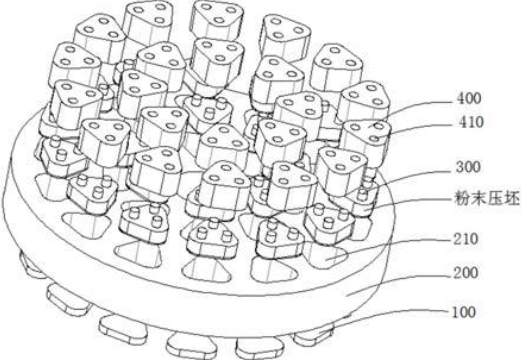
The preparation of PM brake pads involves several key steps:
Powder Mixing: Metal powders and other additives are homogeneously mixed to ensure consistent material properties.
Compaction: The mixture is compacted into a preform using high-pressure molds to achieve the desired shape and density.
Sintering: The compacted preforms are sintered in a controlled atmosphere at high temperatures to bond the particles and improve the mechanical strength and thermal conductivity of the brake pads.
Post-Processing: Depending on the application, the sintered brake pads may undergo additional surface treatments, machining, or quality inspections to meet precise performance standards.
The PM process enables the production of brake pads with highly uniform material properties, ensuring consistent performance under varying operating conditions. The ability to tailor the composition and density of the pads allows for the optimization of friction and thermal properties, enhancing braking efficiency and durability. Moreover, the near-net-shape manufacturing capability reduces material waste and minimizes machining requirements, resulting in cost savings.
Powder metallurgy brake pads are used in a range of applications, from passenger vehicles and high-speed trains to industrial equipment. Their ability to maintain stable friction coefficients, excellent wear resistance, and reliable heat dissipation ensures superior performance under demanding conditions.
The preparation of powder metallurgy brake pads exemplifies the potential of PM technology in delivering high-performance, cost-effective solutions for modern braking systems. As innovations in material science and process engineering continue to evolve, PM brake pads are poised to play an even greater role in future braking applications.
